No more ‘sugar-coating’ on invasive fungus
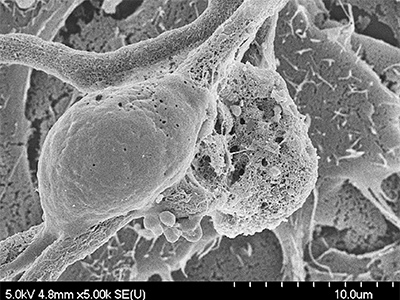
Aspergillus fumigatus colony
Aspergillus fumigatus
Montreal - There are believed to be around 1.5 million different species of fungus on Earth, but one mold, known as Aspergillus fumigatus, causes the majority of cases of invasive aspergillosis – a devastating illness that kills 90 per cent of patients with weakened immune systems or lung diseases. Until now researchers could not explain the virulence of this particular fungus, but a recent discovery by a team of scientists at the Research Institute of the McGill University Health Centre (RI-MUHC) explains why this organism is more dangerous than its relatives. The results of their study, which were published recently in PLOS Pathogens,may be a game changer in the way patients are treated for invasive aspergillosis.
“We found that A. fumigatus was developing a sugar armour that protects it from being killed by our white blood cells, called neutrophils, that usually fight diseases,’’ explains Dr. Donald Sheppard, director of the Division of Infectious Diseases at the MUHC and a professor in the departments of Medicine and Microbiology and Immunology at McGill University. “This is an important discovery because we did not know why A. fumigatus was so virulent in some patients, and now we are starting to develop drugs against this sugar-coating.’’
Aspergillosis is an infection caused by A. fumigatus, a common type of fungus that lives both indoors and outdoors. Most people breathe in A. fumigatus spores every day without getting sick. However, people with weakened immune systems or lung diseases are at higher risk of developing health problems from this fungus. The types of health problems caused by A. fumigatus include allergic reactions, lung infections, and infections in other organs.

Dr. Donald Sheppard, director of the Division of Infectious Diseases at the MUHC and a professor in the departments of Medicine and Microbiology and Immunology at McGill University.
Dr. Sheppard’s team set out to explore features that could facilitate infection by A. fumigatus as compared with less pathogenicAspergillus species. Because they had previously identified a particular sugar in the cell wall of A. fumigatus called GAG (galactosaminogalactan) as critical to the fungus’ ability to outwit the host immune system, the researchers started by testing whether differences in GAG production contribute to differences in the fungus’s ability to cause disease. By manipulating A.fumigatus to make it synthesize more GAG, they made it more virulent.
“We also observed that A. fumigatus, due to this sugar-coating, was able to escape traps produced by neutrophils,’’ explains Dr. Sheppard. Neutrophils respond to an infection by developing a web-like network called Neutrophils Extracellular Traps (NETs), composed of DNA and proteins. The NETs are designed to trap and kill invading pathogens, but the sugar-coating protects A. fumigatus. “Indeed, the sugar-coat repels the NETS and prevents them from binding because both the peptides in the NETs and GAG are positively charged, thus repelling each other. Now that we have highlighted the importance of GAG as a key factor for the ability of A. fumigatus to develop acute lung infection, targeting this sugar armour may be an effective antifungal approach in some patients,’’ concludes Dr. Sheppard.
About the study
The study The Fungal Exopolysaccharide Galactosaminogalactan Mediates Virulence by Enhancing Resistance to Neutrophil Extracellular Traps is available online on PLOS Pathogens. This work was supported in part by Operating funds from the Canadian Cystic Fibrosis Foundation, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, and grant R01AI073829 from the National Institutes of Health, USA. DCS was supported by a Chercheur-Boursier award from the Fonds de recherche du Québec – Santé. MJL was supported by a studentship from the Research Institute of the McGill University Health Centre.
About The Research Institute of the McGill University Health Centre
The Research Institute of the McGill University Health Centre (RI-MUHC) is a world-renowned biomedical and healthcare research centre. The Institute, which is affiliated with the Faculty of Medicine of McGill University, is the research arm of the McGill University Health Centre (MUHC) - an academic health centre located in Montreal, Canada, that has a mandate to focus on complex care within its community. The RI-MUHC supports over 500 researchers, and over 1,200 students, devoted to a broad spectrum of fundamental, clinical and health outcomes research at the Glen and the Montreal General Hospital sites of the MUHC. Our research facilities offer a dynamic multidisciplinary environment that fosters collaboration and leverages discovery aimed at improving the health of individual patients across their lifespan. Over 1,600 clinical research projects and trials are conducted within the organization annually. The RI-MUHC is supported in part by the Fonds de recherche du Québec - Santé (FRQS). www.rimuhc.ca
-30-
Media contact:
Julie Robert
Public Affairs and Strategic Planning
McGill University Health Centre
[email protected]
(514) 934-1934 ext. 71381
@cusm_muhc
muhc.ca|rimuhc.ca